Free and open-source alternative to GitHub Copilot: Continue.dev + Ollama + Visual Studio Code
Instructions to install and use Continue.dev, a FOSS alternative to GitHub Copilot, in Visual Studio Code with Ollama.

Coding assistants like GitHub Copilot have become a standard tool in software development during the AI era, with a recent survey showing that 84% of developers use or plan to use them in 2025. Although the assistance they offer is incredibly helpful, and I have experienced it myself, they also carry several problems: they aren’t private, with all your code and activity being sent to the provider’s servers; they aren’t exactly cheap; and at least the most popular ones are proprietary, with the entire ecosystem being in the hands of a few tech giants.
Fortunately, the increasing availability of open-weight LLM models that can be run locally and offline has also led to the emergence of open-source ecosystems centered around them, and has made it possible to prescind from some of these proprietary and online services (at least if your hardware is powerful enough to run decent local LLMs).
One of these tools is Continue, an open-source alternative to GitHub Copilot that can be connected to local LLM models via Ollama, allowing you to use typical features of AI coding assistants such as code autocompletion and in-IDE chat completely privately and offline.
In this tutorial, I’m going to explain how to install it and configure it in a setup using Ollama and Visual Studio Code.
Installing Ollama
Ollama is an open-source AI model runner, and it’s the one that will host and run the LLM model(s) that will power Continue. You can install it either through its official instructions, or if you use Linux, I recommend following my tutorial to run Ollama on Docker (ignore the Open WebUI step if you wish. You can also replace gpt-oss with your preferred model from Ollama’s library).
After those steps have been followed, Ollama should be running, and the API will be serving at http://localhost:11434, which is where Continue will connect.
Installing Continue
If you’re using Visual Studio Code, install the Continue extension from Visual Studio Marketplace. After it has been installed, it is necessary to configure it to connect to Ollama. For this, consult these pages from the official documentation:
I’m going to summarize here the instructions for Linux:
Let’s create the YAML configuration file:
1
nano ~/.continue/config.yaml
And replace its contents with this:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
name: Local Assistant
version: 1.0.0
schema: v1
models:
# - name: Qwen2.5-Coder 3B
# provider: ollama
# apiBase: http://localhost:11434
# model: qwen2.5-coder:3b
# roles:
# - chat
# - edit
# - apply
# - autocomplete
# - embed
# - name: gpt-oss 20B
# provider: ollama
# apiBase: http://localhost:11434
# model: gpt-oss:20b
# roles:
# - chat
# - edit
# - apply
# - autocomplete
# - embed
context:
- provider: code
- provider: docs
- provider: diff
- provider: terminal
- provider: problems
- provider: folder
- provider: codebase
That file is preconfigured to work with some of the most popular LLM coding models. Uncomment the one(s) of your preference and leave the others commented or remove them, or use any other you want from Ollama’s library (remember that you have to install it first with ollama pull <model>).
With this, Continue should already detect your running models and be ready to work.
Using Continue
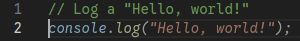
Continue works similarly to GitHub Copilot. If autocomplete is enabled, as in the above file, it will call your local LLM model as you type and output code suggestions:
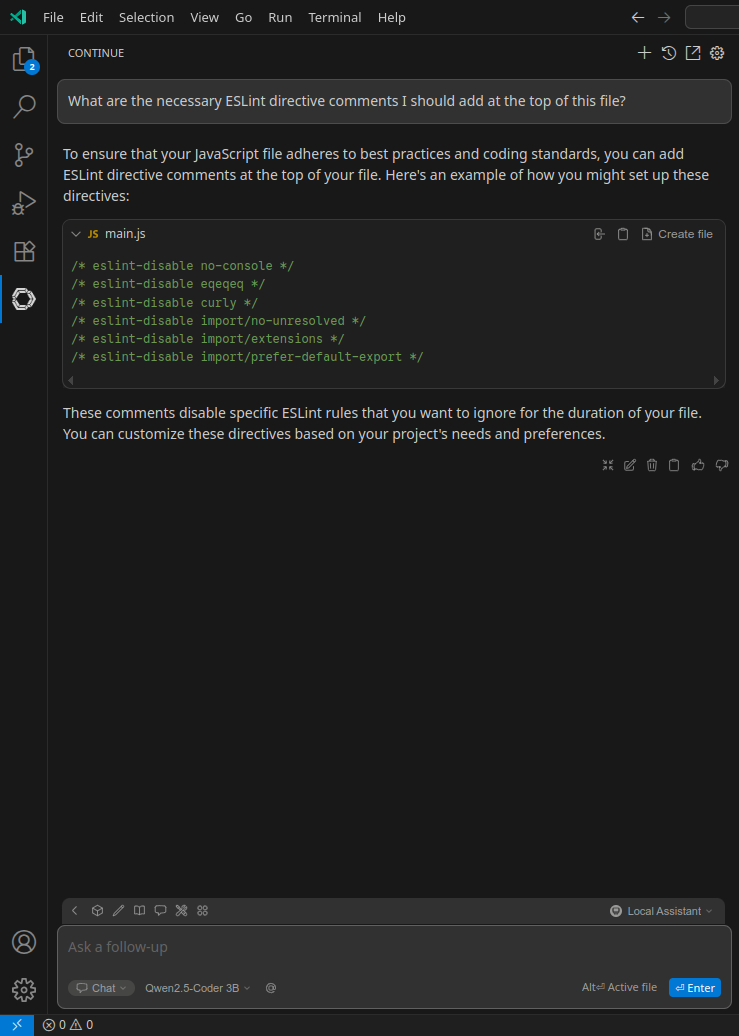
You can also click the Continue icon in the left sidebar and open a chat window to ask questions:
For a complete list of features, consult its documentation.
Keep in mind that the performance will depend on the potency of your hardware and the size and optimization of the model(s) you’re running, and the features can be very slow if you’re running a model too heavy for your hardware capabilities. You may have to experiment to see which model brings the appropriate balance between speed and accuracy.


